ASTM A387 steel plate is a specification for chromium-molybdenum alloy steel plates intended primarily for use in elevated temperature service. These plates are designed for applications that require improved mechanical properties and resistance to oxidation, making them suitable for use in high-temperature environments.

Key Properties:
- Composition: ASTM A387 steel plates typically contain chromium (up to 9% or more) and molybdenum (up to 2.25% or more), which enhance their strength and corrosion resistance at high temperatures.
- Grades: The specification includes various grades, such as Grade 5, 9, 11, 12, 22, and 24, differentiated by their composition and intended use.
Applications:
ASTM A387 steel plates are commonly used in:
- Pressure vessels
- Heat exchangers
- Power generation equipment
- Piping systems in the oil and gas industry
- Chemical processing facilities
Overall, ASTM A387 steel plates are essential for applications requiring materials that can withstand high temperatures and corrosive environments, offering reliable performance and durability.
Chrome moly plates under ASTM A387 are available in several grades with varying alloy compositions. The commonly used grades include Gr 11, Gr 22, Gr 5, Gr 9, and Gr 91.
Grade | Nominal Chromium Content, % | Nominal Molybdenum Content, % |
|---|---|---|
2 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
12 | 1.00 | 0.50 |
11 | 1.25 | 0.50 |
22, 22L | 2.25 | 1.00 |
21, 21L | 3.00 | 1.00 |
5 | 5.00 | 0.50 |
9 | 9.00 | 1.00 |
91 | 9.00 | 1.00 |
With the exception of Grades 21L, 22L, and 91, each grade is offered in two classes based on tensile strength levels as outlined in the tensile requirements tables. Grades 21L and 22L are available only in Class 1, while Grade 91 is available solely in Class 2.
Refered Standards for ASTM A387 Alloy Steel Plate
ASTM
- A20/A20M: General requirements for pressure vessel plates.
- A370: Test specification for mechanical properties of steel
- A435/A435M: For straight-beam ultrasonic examination of steel plates
- A577/A577M: For ultrasonic angle beam examination of steel plates
- A578/A578M: For straight beam UT examination of rolled steel plates in special applications
- A1017/A1017M: Specification for pressure vessle plates of alloy steel, chromium-molybdenum-tungsten
AWS Specification
- A5.5/A5.5M: Low alloy steel electrodes for shield metal arc welding.
- A5.23/A5.23M: Low alloy steel electrodes for fulxes for submerged arc welding.
- A5.28/A5.28M: For gas shielded arc welding
- A5.29/A5.29M: For flux cored arc welding.
A387 Chrom Moly Plate Data Sheet
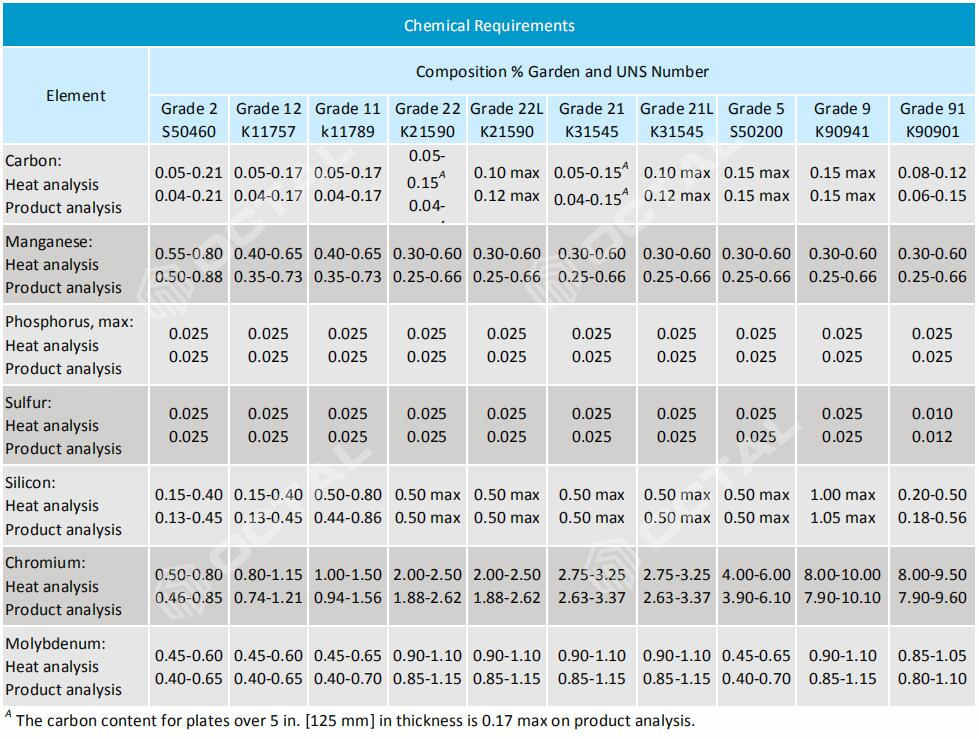
Chemical Composition
Table 1: For A387 Gr 11, 22, 5, 9, 91 Chrome Alloy Steel Plate
Mechanical Properties
Table 2: For A387 Class 1 Chrome Alloy Steel Plates:
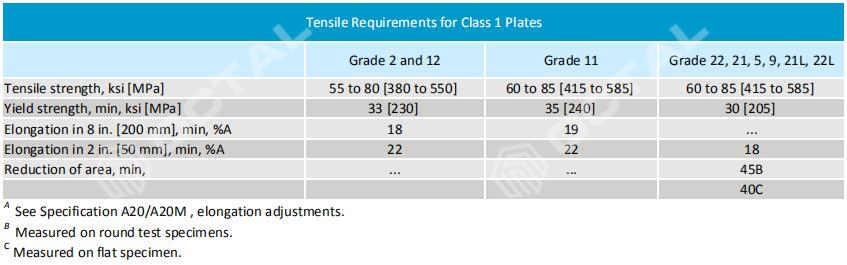
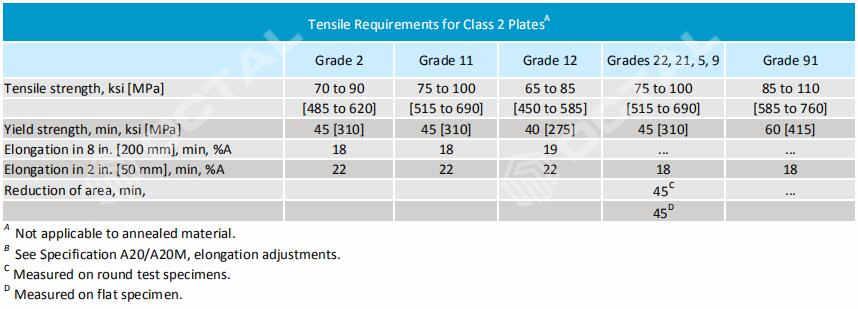
Table 3: For A387 Class 2 Alloy Steel Plates:
Heat Treatment for A387 Chrom Moly Alloy Steel Plate
Chrome moly alloy steel plates under ASTM A387 must be killed steel and are thermally treated through processes such as annealing, normalizing, and tempering. Alternatively, if agreed upon by the buyer, the plates may undergo accelerated cooling from the austenitizing temperature via air blasting or liquid quenching, followed by tempering. The minimum tempering temperatures are outlined in the table below:
Grade | Temperature, °F [°C] |
|---|---|
2, 12 and 11 | 1150 [620] |
22, 22L, 21, 21L and 9 | 1250 [675] |
5 | 1300 [705] |
Grade 91 alloy steel plates shall be heat treated by normalizing and tempering or by accelerated cooling by air blasting or liquid quenching, followed by tempering. Grade 91 plates need to be austenitized at 1900 to 1975°F [1040 to 1080°C] and shall be tempered at 1350 to 1470°F [730 to 800°C]
Grade 5, 9, 21, 21L, 22, 22L, and 91 plates ordered without heat treatment by above table, shall be finished in either the stress relieved or annealed condition.
Dfferemce between ASTM A387 Grade 11 and Grade 22
ASTM A387 Grade 22 Plate Specification
Comparison between ASTM A387 Grade 11 and Grade 22:
Composition:
- Grade 11: Contains approximately 1% chromium and 0.5% molybdenum.
- Grade 22: Contains about 2.25% molybdenum and 1% chromium. This higher molybdenum content enhances its strength and resistance to high temperatures.
Mechanical Properties:
- Grade 11:
- Minimum yield strength: 205 MPa (30,000 psi)
- Minimum tensile strength: 415 MPa (60,000 psi)
- Grade 22:
- Minimum yield strength: 240 MPa (35,000 psi)
- Minimum tensile strength: 550 MPa (80,000 psi)
Applications:
- Grade 11: Primarily used in applications requiring moderate strength at elevated temperatures, such as in boilers and pressure vessels.
- Grade 22: Typically used in more demanding applications where higher strength and resistance to creep are needed, including in power generation and chemical processing systems.
Summary:
The main differences between ASTM A387 Grade 11 and Grade 22 lie in their composition, mechanical properties, and intended applications. Grade 22 generally offers better performance under high temperatures and stress due to its higher molybdenum content, making it suitable for more critical applications compared to Grade 11.